About Sparse-Plex¶
Sparse-plex is a MATLAB library for solving sparse representation problems.
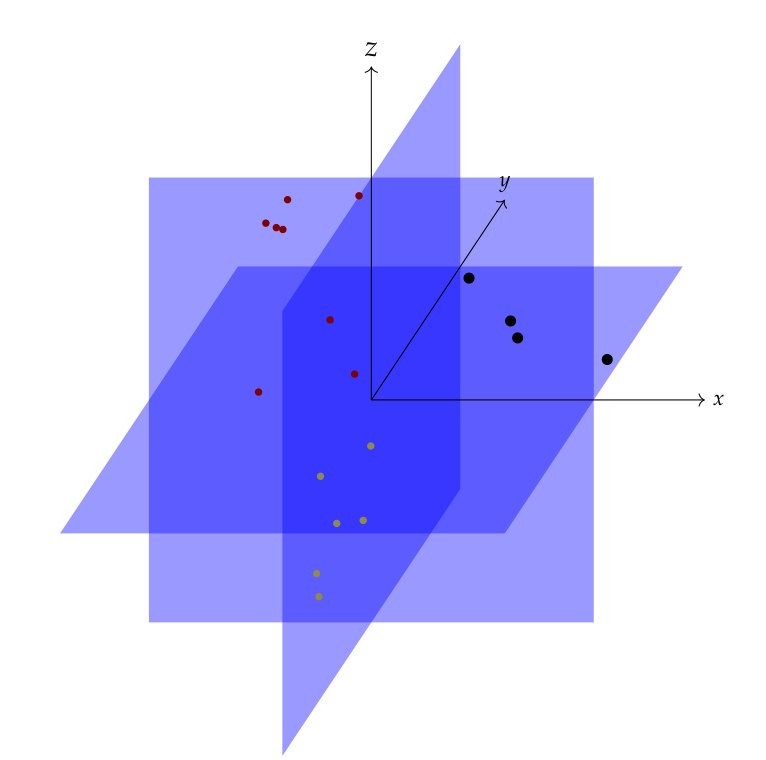
This is an example of a union of subspaces model. While the ambient space is \(\RR^3\), the data points actually fall in one of the three 2-d planes. The black points are in \(xy\)-plane, yellow points in \(yz\)-plane and red points in \(zx\) plane. Each of the 3 planes is a subspace of the ambient 3 dimensional space. Once an appropriate basis for each of the subspaces is chosen, the data points require only 2 coordinates to identify them in the subspace. In this case, it is easy to see that the standard basis for \(\RR^3\) contains the basis vectors for individual subspaces also. Thus, in the standard basis, each data point has only 2-non-zero coordinates.
The library website is : http://indigits.github.io/sparse-plex/.
Online documentation is hosted at: http://sparse-plex.readthedocs.org/en/latest/.
The project is hosted on GITHUB at: https://github.com/indigits/sparse-plex.
It contains implementations of many state of the art algorithms. Some implementations are simple and straight-forward while some have taken extra efforts to optimize the speed.
In addition to these, the library provides implementations of many other algorithms which are building blocks for the sparse recovery algorithms.
The library aims to solve:
- Single vector sparse recovery or sparse approximation problems
- Multiple vector joint sparse recovery or sparse approximation problems
The library provides
- Various simple dictionaries and sensing matrices
- Implementations of pursuit algorithms
- Matching pursuit
- Orthogonal matching pursuit
- Compressive sampling matching pursuit
- Basis pursuit
- Some joint recovery algorithms
- Cluster orthogonal matching pursuit
- Some clustering algorithms
- Spectral clustering
- Sparse subspace clustering using l_1 minimization
- Sparse subspace clustering using orthogonal matching pursuit
- Various utilities for working with matrices, signals, norms, distances, signal comparison, vector spaces
- Some visualization utilities
- Some combinatoric systems
- Various constructions for synthetic sparse signals
- Some optimization algorithms
- steepest descent
- conjugate gradient descent
- Detection and estimation algorithms
- Compressive binary detector
The documentation contains several how-to-do tutorials. They are meant to help beginners in the area ramp up quickly. The documentation is not really a user manual. It doesn’t describe all parameters and behavior of a function in detail. Rather, it provides various code examples to explain how things work. Users are requested to read through the source code and relevant papers to get a deeper understanding of the methods.